OpenSearch 2.2 is now available!
OpenSearch 2.2 is ready to download! This release includes 23 new features and 12 enhancements to help you build and optimize your solutions for search, analytics, and observability workloads. Following are some highlights of the capabilities you can use to advance machine learning (ML) models, data visualizations, cluster resiliency, and more. As always, the release notes provide further details.
Update: On August 12 the OpenSearch project published a security advisory for a vulnerability in the software’s security plugin. The vulnerability allows requests to access sensitive information when the customer has acted to restrict access that specific information. This issue has been fixed in OpenSearch 2.2.0. Users of 2.0.0 or 2.1.0 versions are encouraged to upgrade to version 2.2.0 to resolve the vulnerability.
New ML features and algorithms
Logistic Regression: This release extends OpenSearch’s ML capabilities with the addition of a logistic regression algorithm to the ML Commons plugin. Often, logistic regression is used to model a binary outcome (something that can take two values, such as “yes/no” or “true/false”) to solve a classification problem, such as predicting whether a new sample best fits a particular category. This supports a number of interesting use cases in areas such as natural language processing, recommendation systems, fraud detection, and more.
Lucene HNSW Implementation: The 2.2 release benefits from the project’s collaboration with the Lucene community with the addition of Lucene’s implementation of the hierarchical navigable small worlds (HNSW) algorithm for approximate k-NN search. Now OpenSearch users have a choice between Lucene-based k-NN search, which is platform independent, and the C-based libraries Non-Metric Space Library (Nmslib) and Facebook AI Similarity Search (Faiss), which users find well-suited for high-performance, highly scalable workloads.
RCFSummarize Algorithm: This release also introduces a new clustering algorithm, RCFSummarize, that enables users to cluster data into similar groups. The RCFSummarize clustering technique is different from traditional k-means algorithms in that it does not require you to specify a k value for the number of categories. Instead, it will adaptively find out the real k, making it easier to get insights from your data.
Other updates in OpenSearch 2.2 include the following.
Search by Relevance: With OpenSearch 2.2, users can now search their indexes for documents by the relevance of the input query using Structured Query Language (SQL) or Piped Processing Language (PPL). This update gives users another approach to generating relevance-based searches along with the option of using OpenSearch query domain-specific language (DSL). For a comprehensive view of the relevance-based functions and search parameters now available in the SQL plugin, check out the feature’s documentation.
Awareness Attribute: In order to make sure OpenSearch clusters are well balanced and resilient to failures in a zone or rack, a new configuration option has been added. Enabling routing.allocation.balance.awareness will ensure that the number of replicas is, at maximum, a multiple of the two awareness attributes cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.attributes and cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.force.zone.values. See our documentation regarding cluster formation for more information.
Custom GeoJSON Support in Region Maps: Until 2.2, region maps in OpenSearch Dashboards had support for a limited set of vector maps for visualization. This feature now provides the ability to upload your own custom region in GeoJSON format and use it as a vector map for visualizations in OpenSearch Dashboards. It also provides the option to draw your own geographic boundaries on a visualization. If you’re unfamiliar with GeoJSON, get your start here.
Data Rollup Enhancements: For data analytics workloads, older time series data can support valuable insights; however, retaining complete datasets as they age can lead to increased storage costs. In 2.2, OpenSearch adds several rollup enhancements that let you roll up aggregated results from older data to dynamic target indexes with the use of a Mustache template. Along with this, you can also now run one search query across multiple target indexes. You can use these features to keep mining value from older time series data while reducing data granularity and lowering the cost burden.
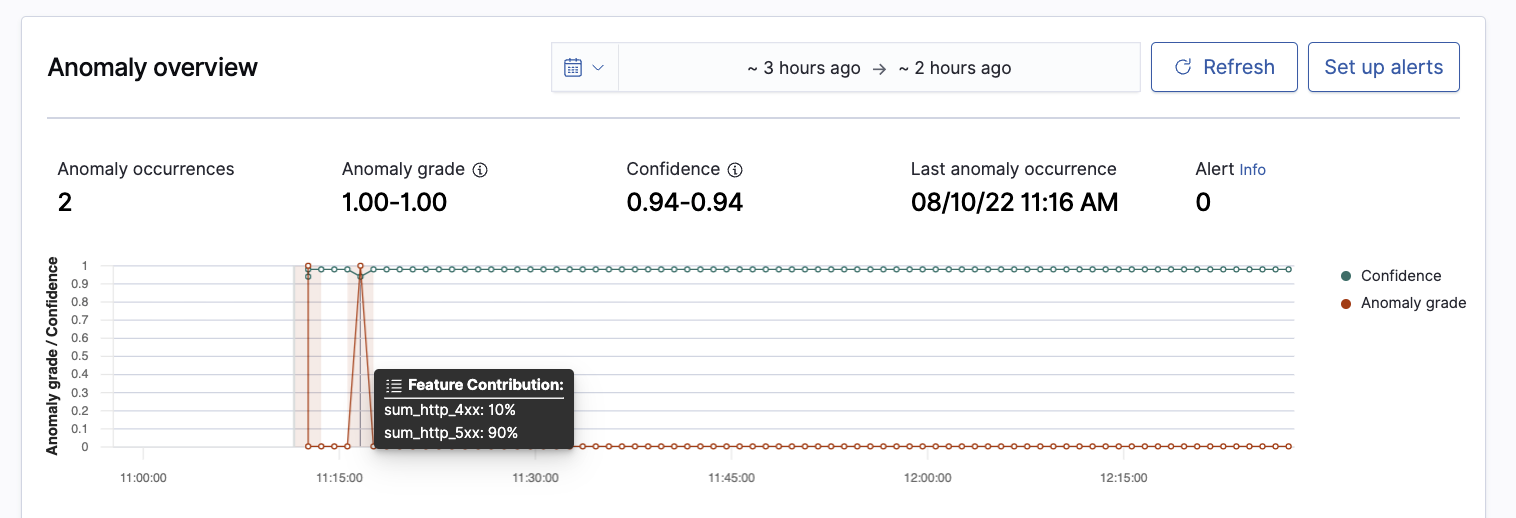
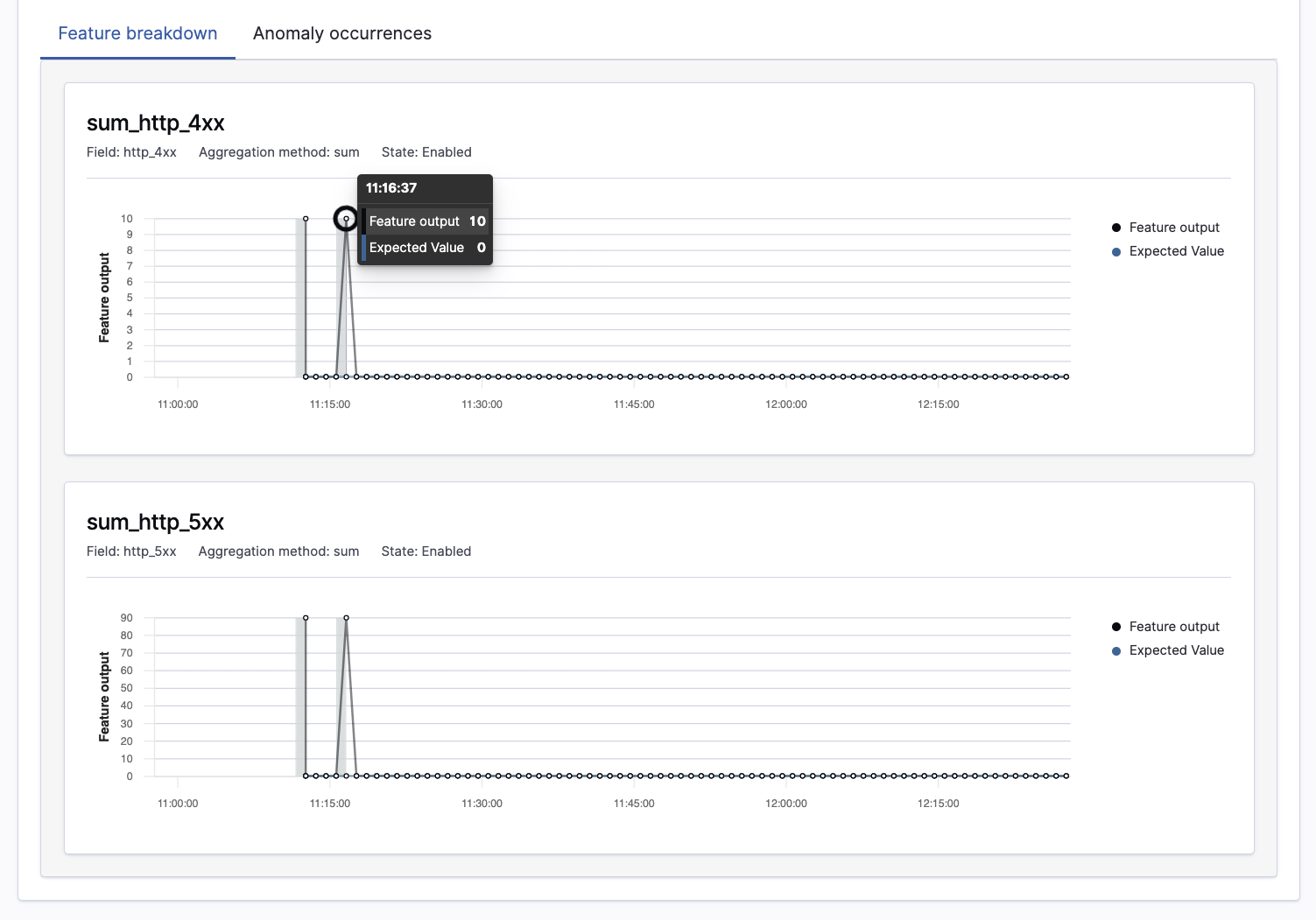
Feature Attribution on Anomaly Details Page: OpenSearch added feature attribution and expected value to its anomaly detection functionality in version 1.2. Today’s release introduces a new user experience that makes it easier to understand what data is driving anomalies. With this update, feature attribution and expected value are exposed on the anomaly detection details page, as seen in the example below.
Get started
OpenSearch 2.2 is ready for download here! Take a look at the latest documentation and release notes, and keep an eye on the OpenSearch Project roadmap for exciting features and enhancements coming in version 2.3!





