Feature Deep Dive: OpenSearch SQL - Basic queries
In this post, we’ll explore some of the features and capabilities supported by OpenSearch SQL. We also briefly introduce how SQL engine works internally.
What is OpenSearch SQL?
OpenSearch SQL is similar to the SELECT statement in ANSI SQL, but it is purely designed for analyzing data in OpenSearch. In this document, we refer to it as OSQL (short for OpenSearch Structured Query Language). In order to make it easier for traditional SQL user to get started, we make the OSQL syntax conform to the subset of the ANSI SQL specification. In addition, we also disclosed the unique features of OpenSearch, for example, we support full-text search.
How to use OpenSearch SQL?
For OpenSearch users, you could use the familiar REST interface _plugin/sql with your query in HTTP body .
For DBMS users, you could use JDBC/ODBC driver to connect OpenSearch domain.
For Dashboards users, you could use OpenSearch Dashboard Query Workbench to easily run on-demand SQL queries and download results.
An additional OpenSearch SQL CLI tool is provided for interactive SQL execution.
Some Examples
Basic Queries
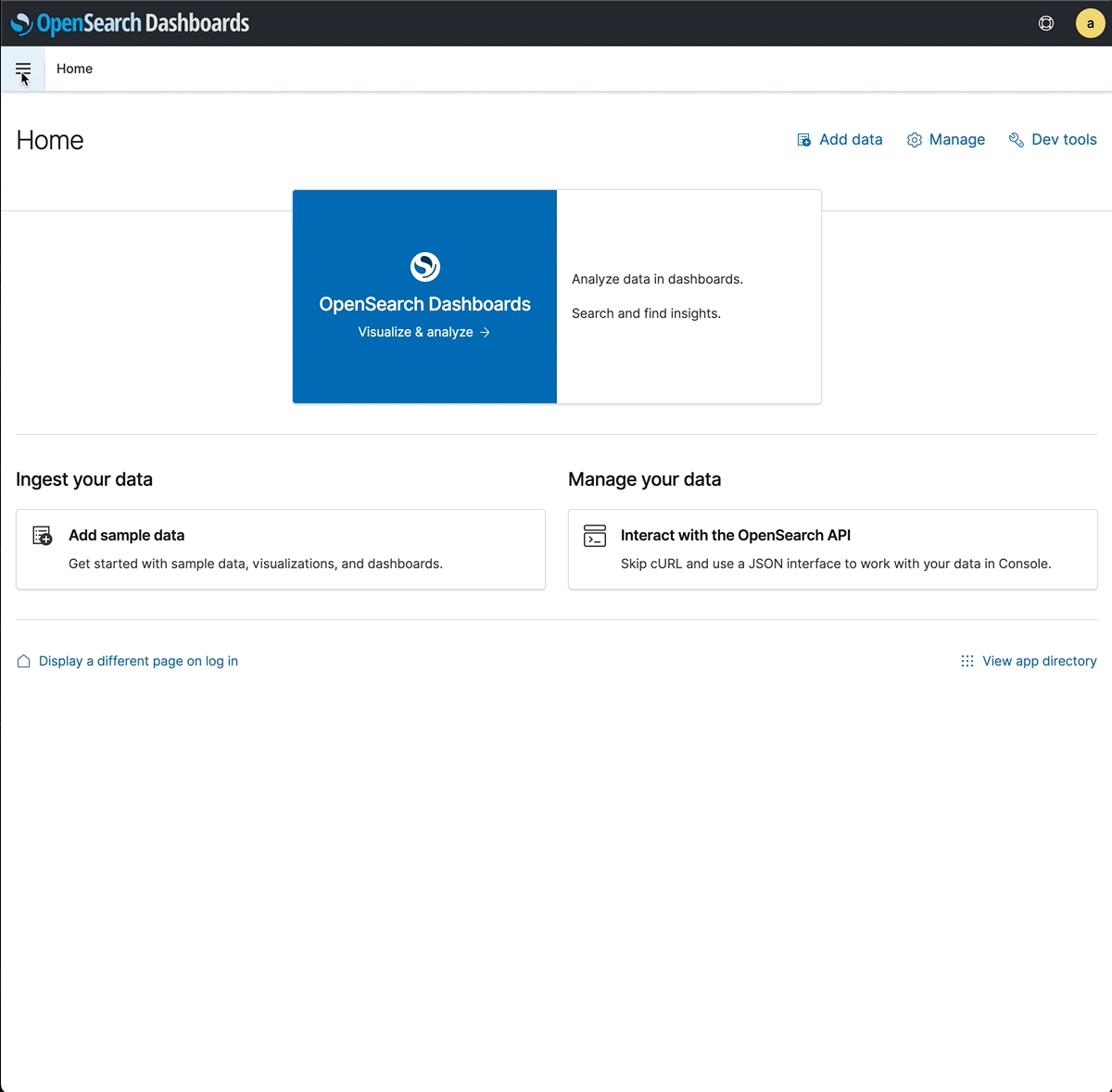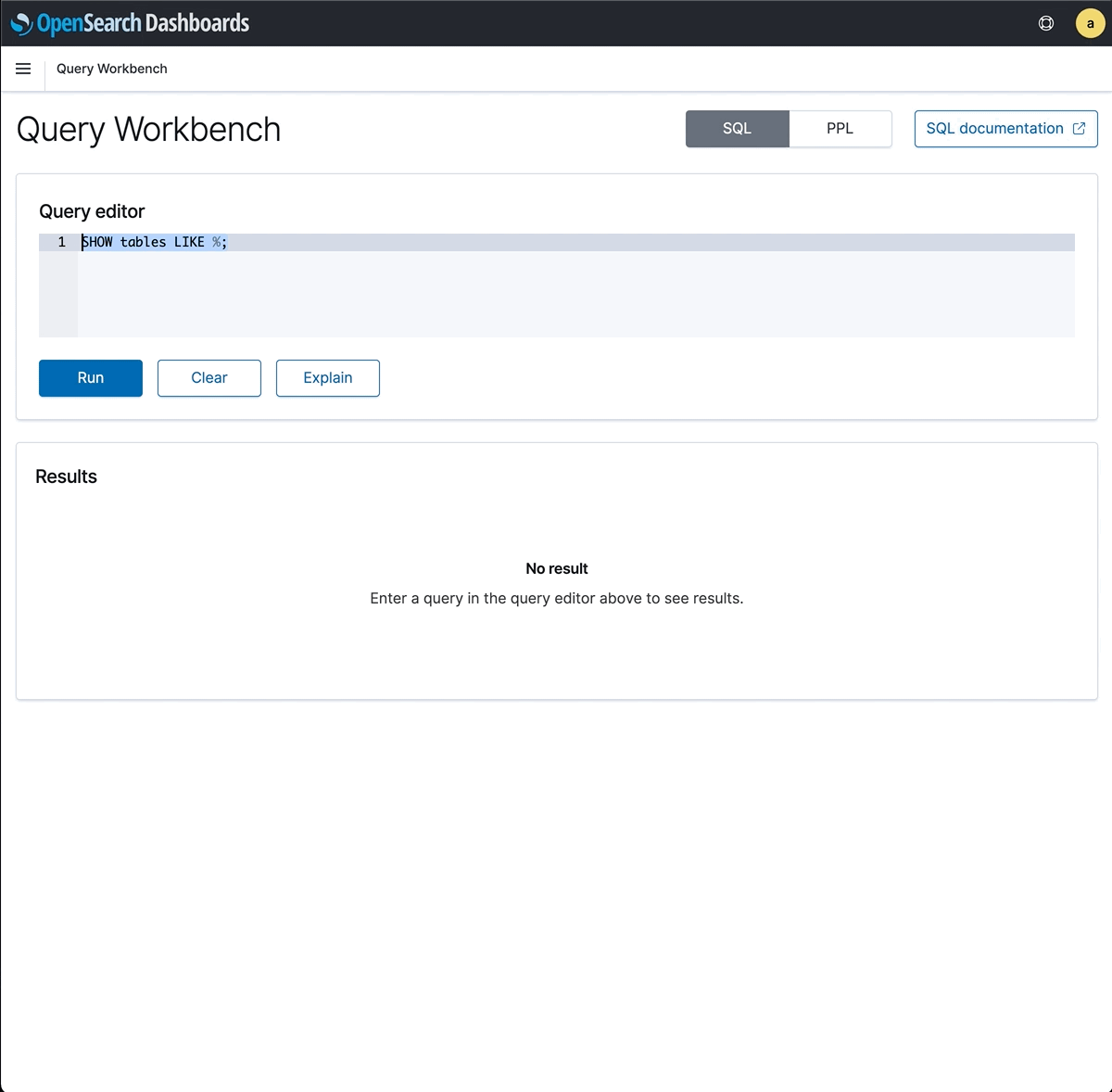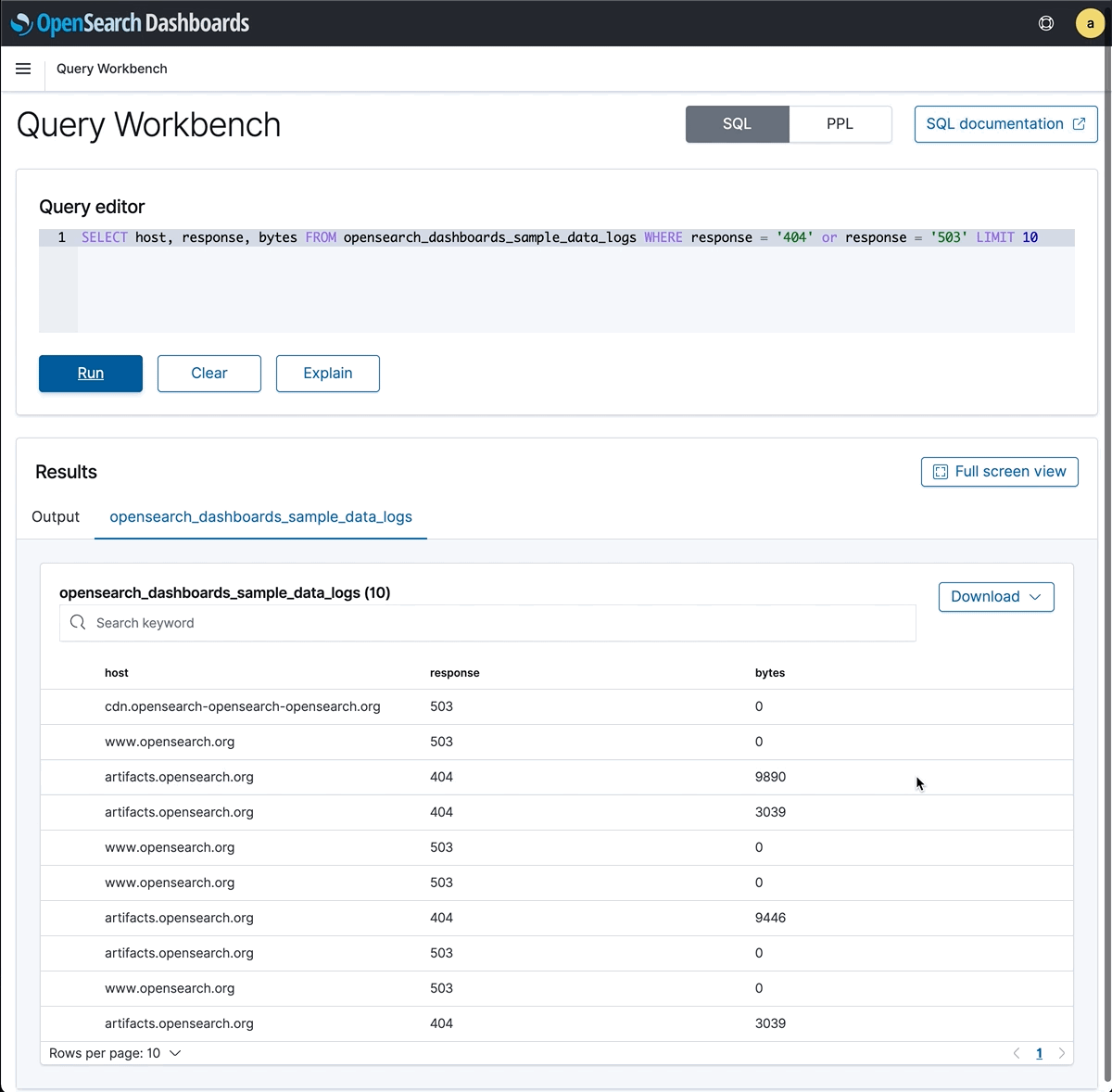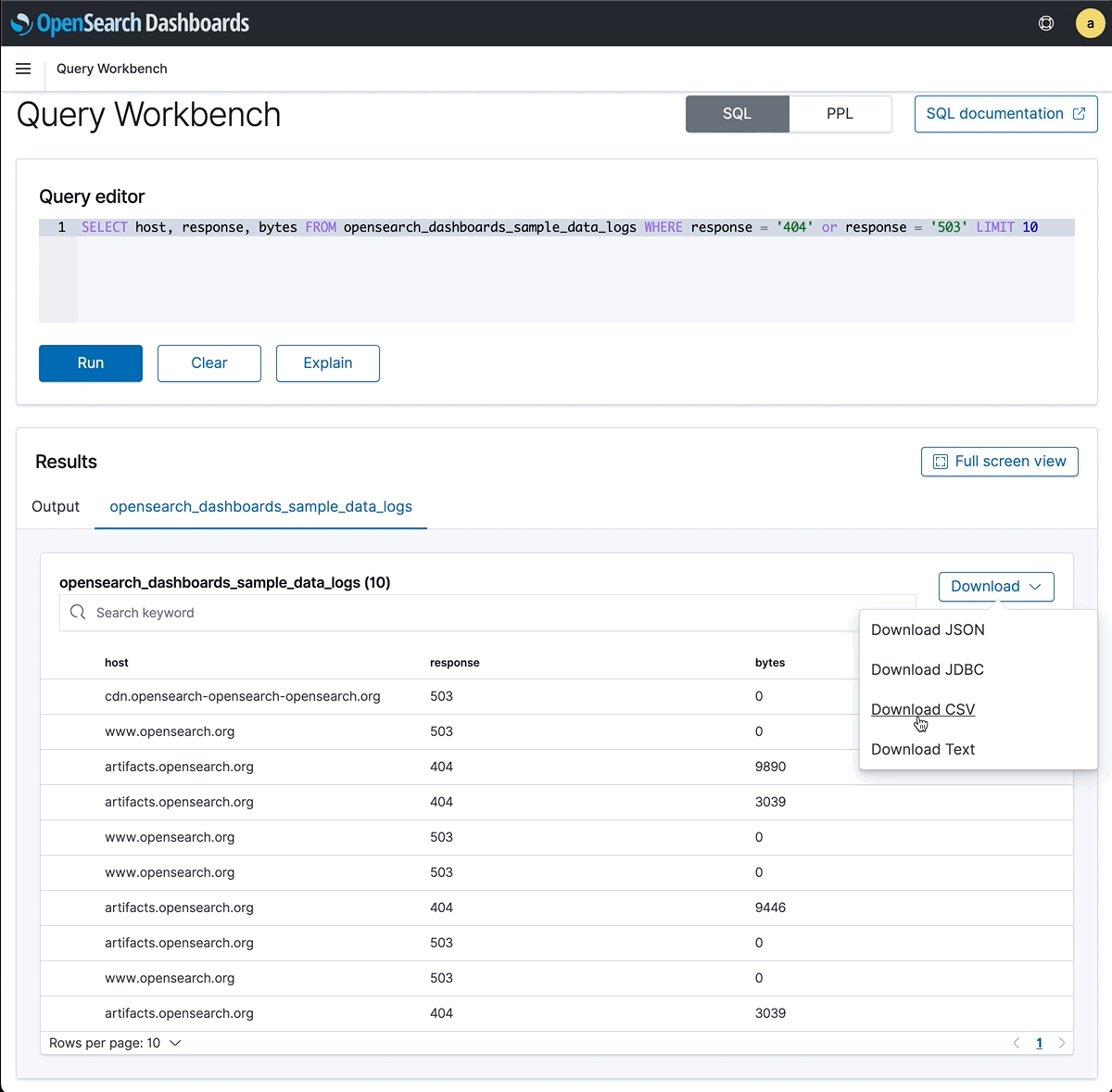
“Find error logs where response code is 404 or 503”.
You can run OSQL in Query Workbench. The results are in tabular format. You could download result in JSON, JDBC, CSV and Text format. More examples are on Github.
Functions
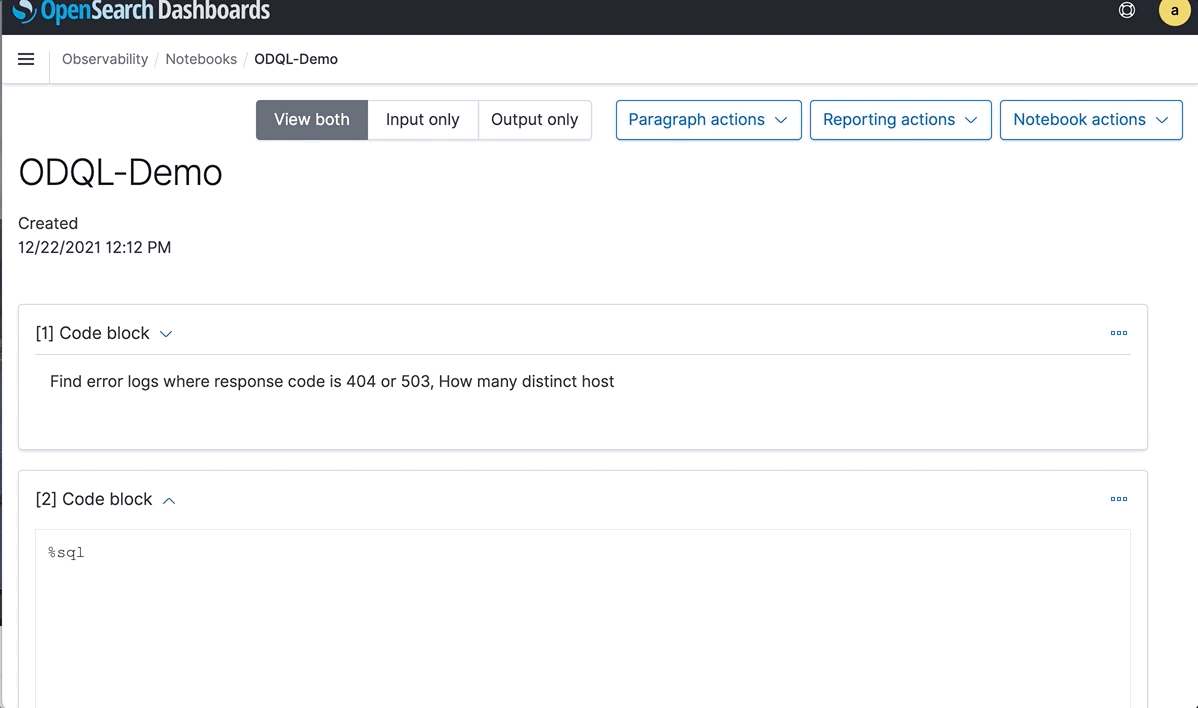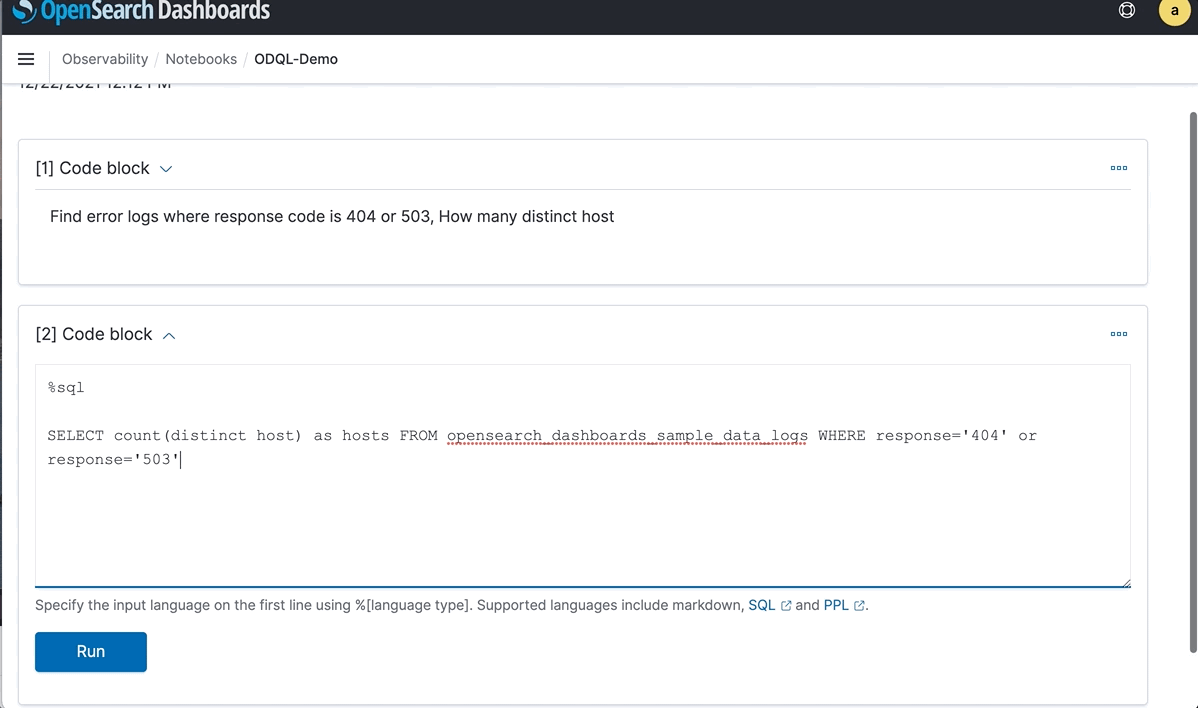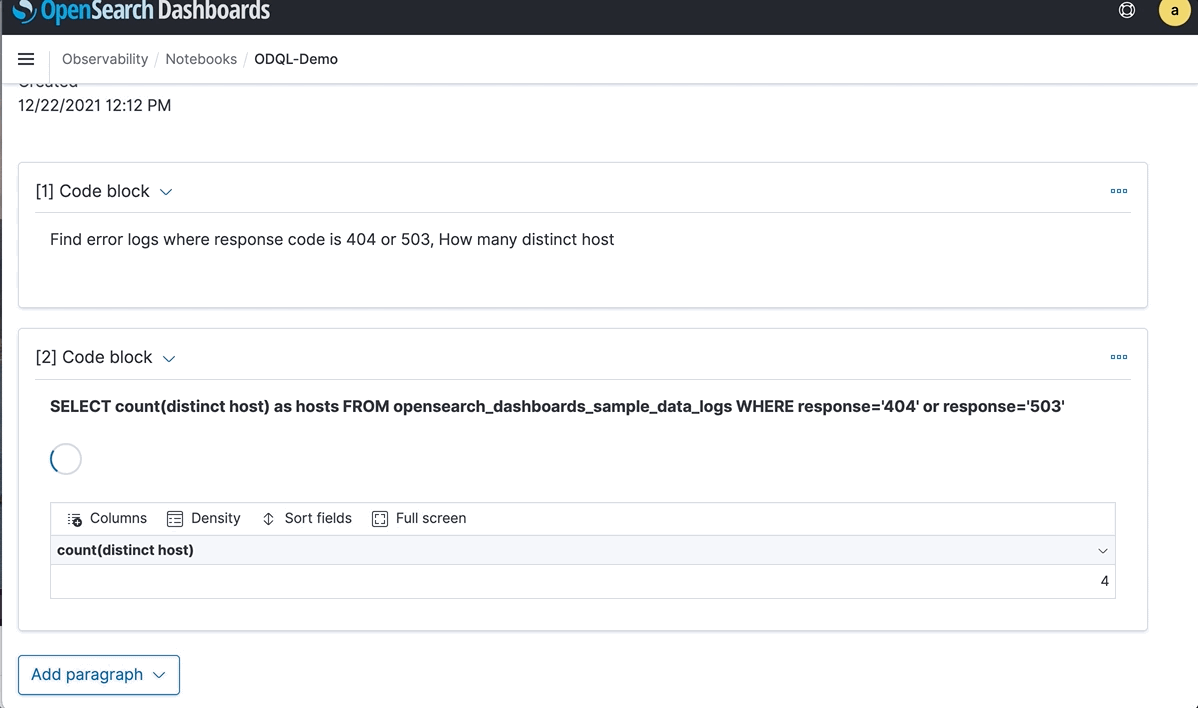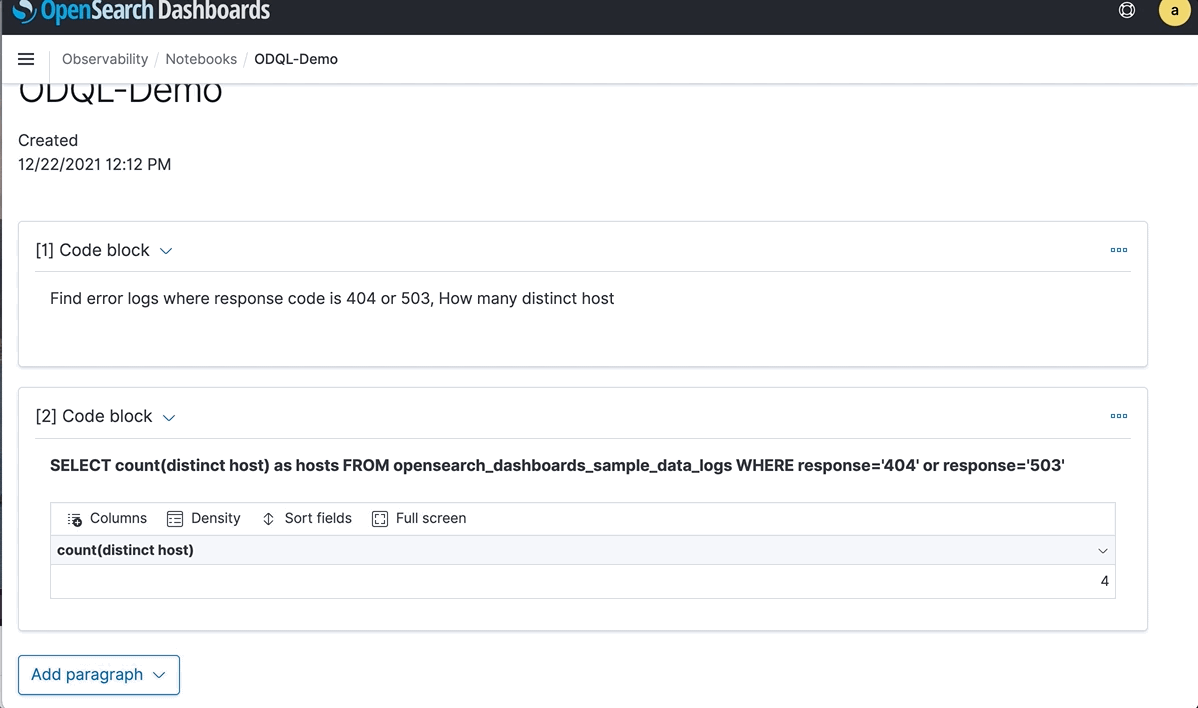
“Find error logs where response code is 404 or 503, How many distinct host”
You could also run OSQL from a OpenSearch Dashboards notebook. In this case, there are four distinct hosts and the results are in table format. More aggregations and functions are supported.
Explain
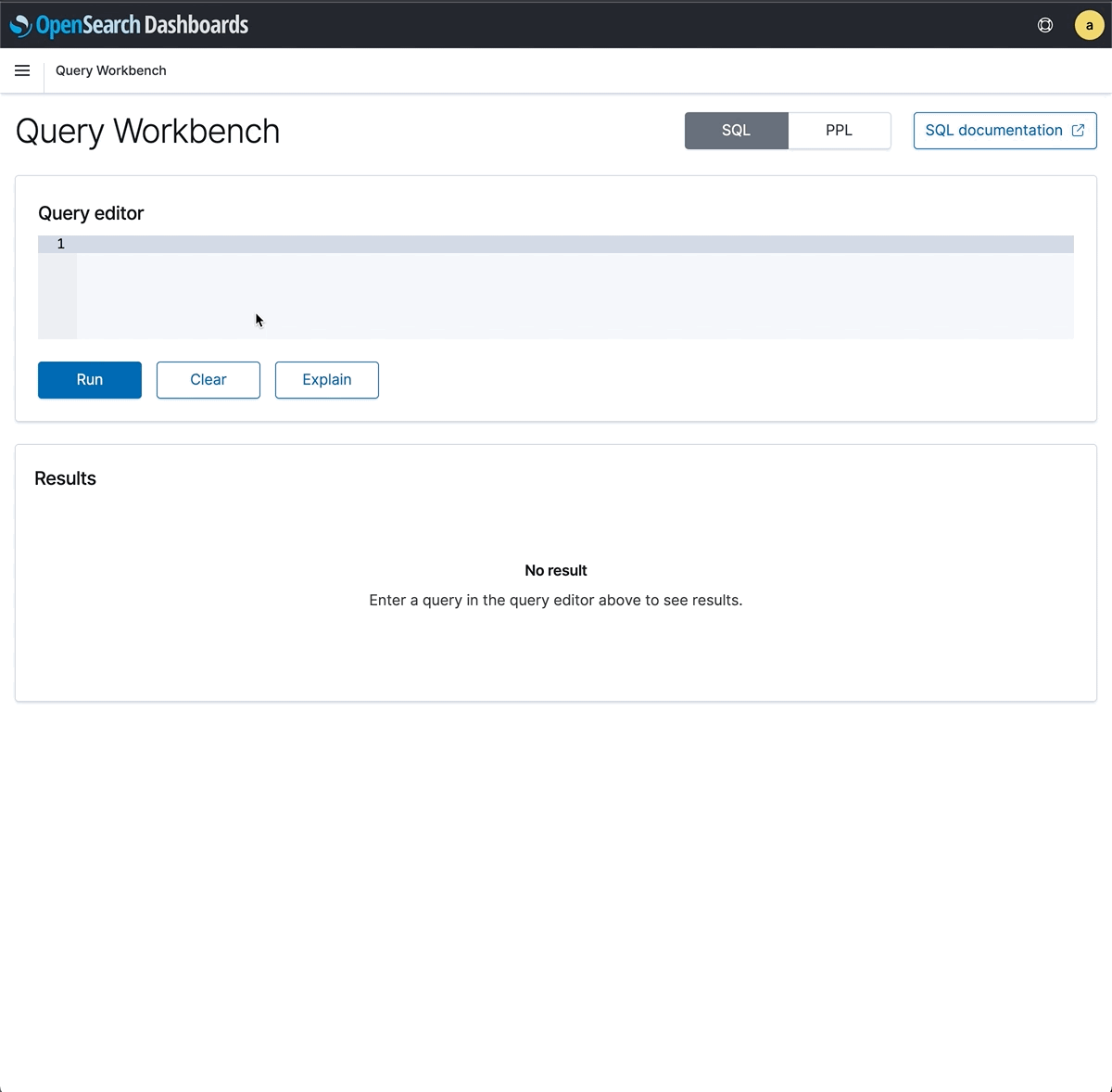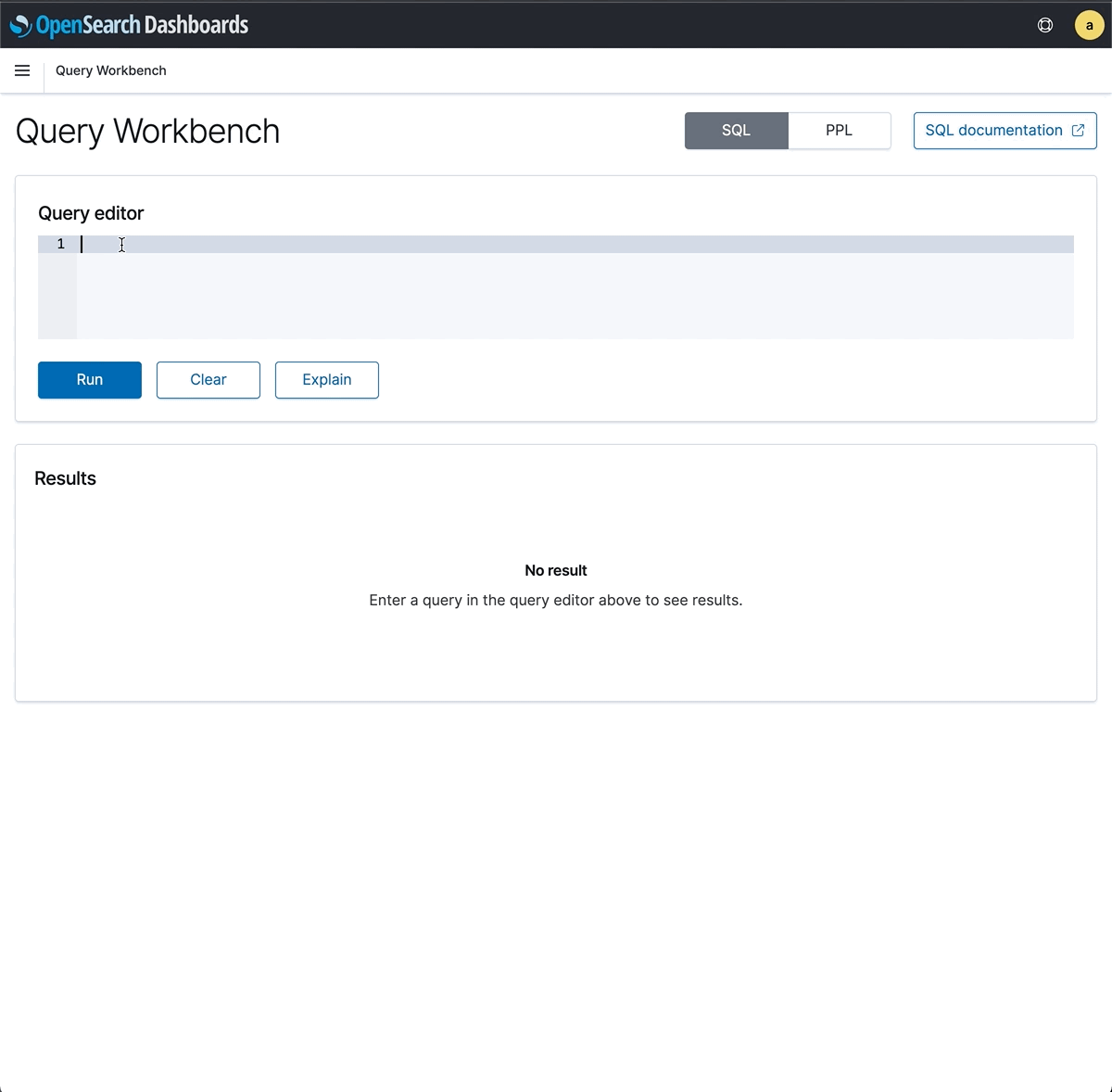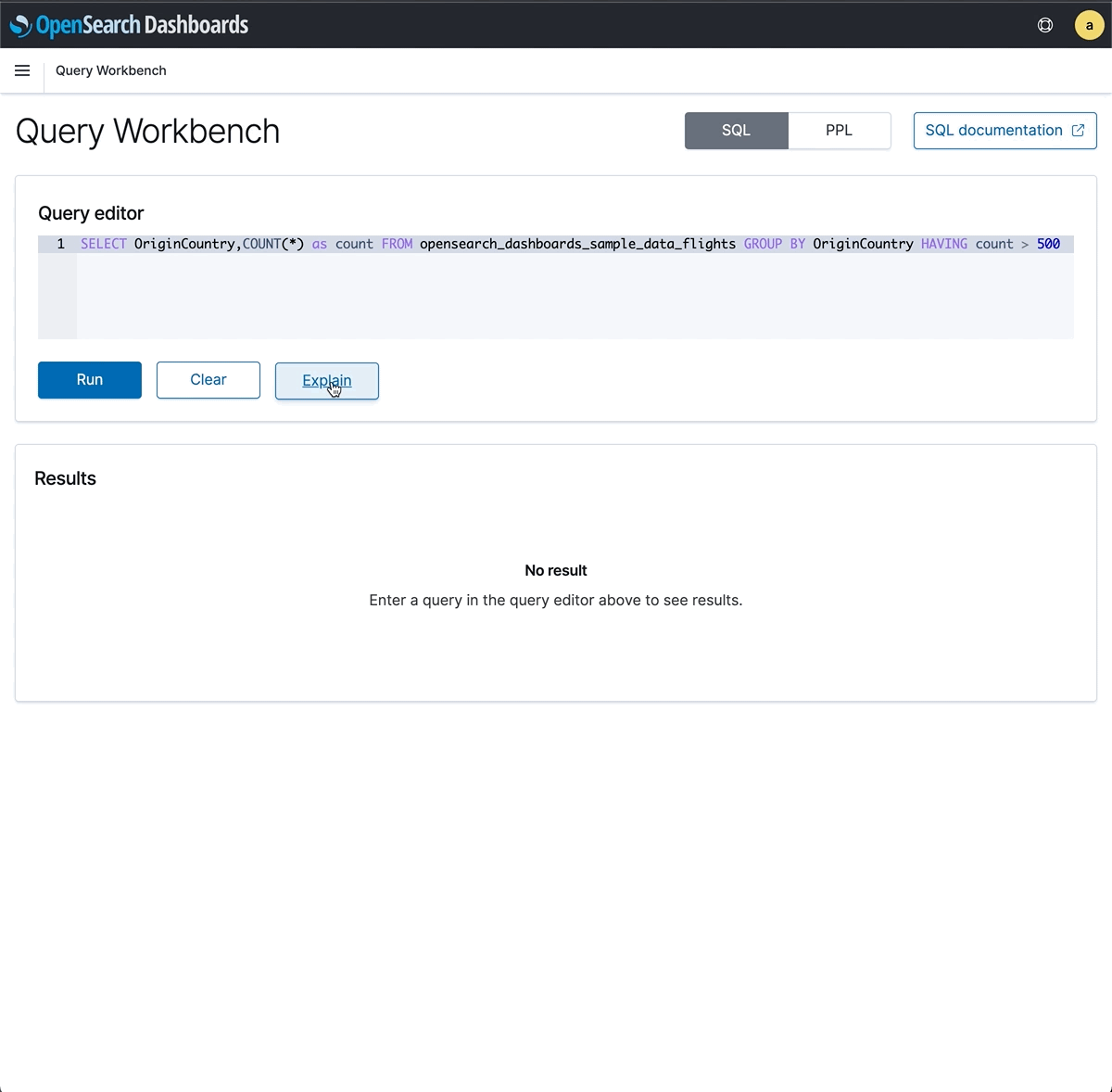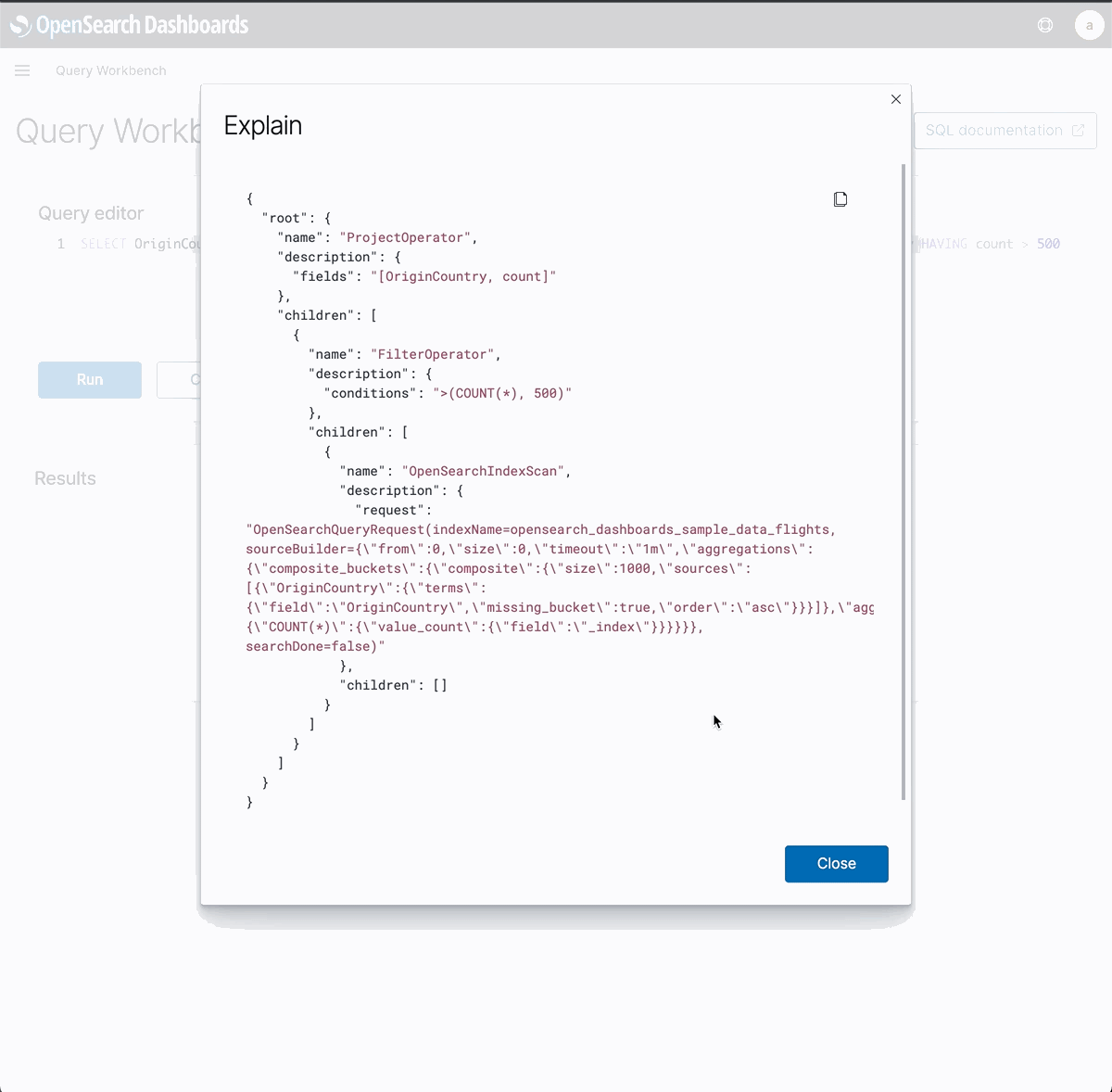
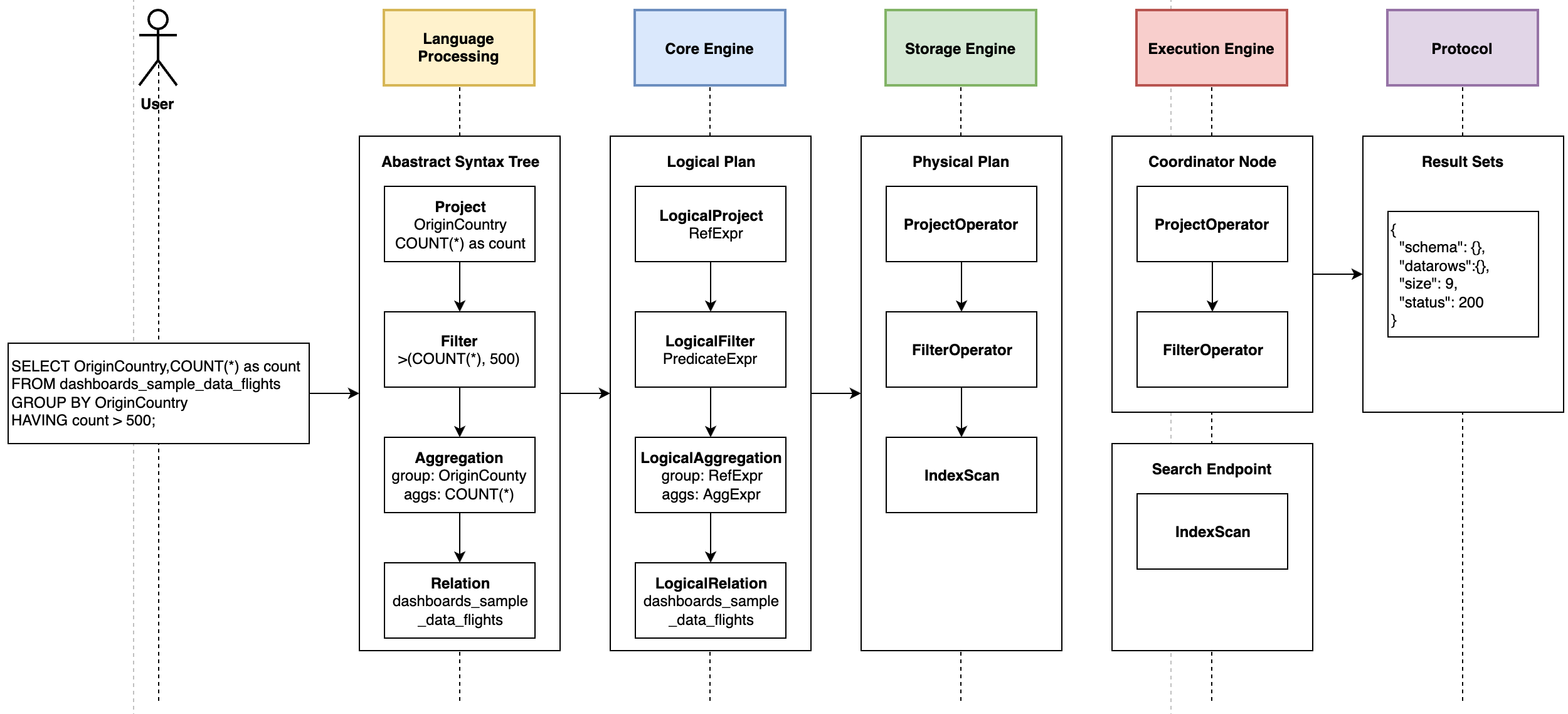
“How does OSQL execute in OpenSearch?”. The OpenSearch SQL explain endpoint returns the query execution plan. For example, here are the three query operators for the above query.
ProjectOperator, execute in coordinate node, read output from child operator and projectoriginCountryandcountfields.FilterOperator, execute in coordinator node, read output from child operator and filter docs whichcount > 500.OpenSearchIndexScan, it is a DSL query which will be executed in OpenSearch through search endpoint.
Inside SQL Engines
Internally, a query will go through five major components in the query engine. (1) Language Processor parses the query string by following the grammar and generates the AST (Abstract Syntax Tree). (2) Core Engine analyzes and optimizes the AST and builds the Logical Plan. (3) Storage Engine is a pluggable component which provides the catalog schema and storage specified optimization and implementation. (4) Execution Engine schedules and executes the physical plan. (5) Protocol parses the request and formats the response.
How do I contribute?
If you’re interested in contributing please reach out on GitHub issues or the community forum. The more formal contribution guidelines are documented in the contributing guide.




