Meet OSCAR: The AI chat assistant that makes OpenSearch releases easier for everyone
OpenSearch is an open-source search and analytics platform that powers website search, log analytics, and application monitoring. It brings together the OpenSearch core engine, OpenSearch Dashboards for visualization, and a growing suite of plugins for a wide variety of end-user applications.
The OpenSearch Project is community driven. Since the project was adopted by The Linux Foundation in September 2024, repositories have expanded from 120+ to 170+, active contributors have risen from 1000+ to 3,500+, and total downloads have exceeded 1.1 billion.
As OpenSearch grows, release management becomes increasingly complex. Release issues need to ship on time and involve multiple components, extensive testing, and careful orchestration every eight weeks. The OpenSearch Engineering Effectiveness (OSEE) team helps the community run releases, resolves engineering issues, and removes bottlenecks and inefficiencies across the project.
Traditionally, the release process has relied heavily on manual intervention from engineers, resulting in time-consuming cycles in which release managers navigate numerous workflows, interpret complex metric data, and coordinate communications across multiple stakeholders in Slack channels.
This inefficient approach presented several challenges:
- High barrier to entry: New release managers required extensive onboarding and deep system knowledge.
- Manual processes: Repetitive tasks consumed valuable engineering time.
- Knowledge gaps: Critical release information was scattered across different systems and team members.
- Community participation: External contributors struggled to participate in release management due to its complexity.
By eliminating this tedious manual work, we’ve made the OpenSearch release process truly accessible to everyone. This means that whether you’re a seasoned engineer or a new community member, you can contribute to a release without domain-specific knowledge. This new release process is about opening doors and making collaboration easier for all.
Why AI is the solution
Modern AI capabilities, particularly those of large language models (LLMs) and conversational interfaces, offer a transformative approach to these challenges. AI can serve as an intelligent bridge between complex systems and human maintainers, contributors, and infrastructure engineers, translating natural language requests into precise technical operations while maintaining security and audit trails.
This trend is already evident within the OpenSearch Project: features like neural search, the machine learning (ML) framework, and OpenSearch’s own Model Context Protocol (MCP) server have transformed data interaction and task automation, replacing traditional methods with more intelligent, automated approaches. Inspired by these successes, the OSEE team recognized that similar technology could help eliminate release bottlenecks and improve our own workflows.
Creating an autonomous agent that serves as the single source of truth (and interaction) for release contributors largely reduces the manual context-switching overhead for all participants. By using AI, access to sophisticated release management capabilities is democratized, reducing workload on engineers and creating a more inclusive environment for community contributors.
Introducing OSCAR
OSCAR (OpenSearch Conversational Automation for Releases) is a multi-agent-powered AI chatbot that helps democratize the OpenSearch release process by providing intelligent assistance, domain-specific knowledge retrieval, metrics and performance information, workflow automation, and general contextual support to the OpenSearch community. Its ultimate goal is end-to-end release orchestration: reducing repetitive work, summarizing detailed metrics into clear reports, and making it easier for external contributors to act as community release managers.
Here’s what OSCAR can do:
- Show current test status or failures for a repository
- Help with release documentation tasks that run alongside code and testing
- Kick off a standard release workflow
OSCAR reduces repetitive work, brings shared procedures into one place, and makes it easier for community members to take on release tasks, with a plan for broader release management.
What stayed the same
- Quality bars: Code review, integration and compatibility tests, and performance checks still apply.
- Humans in charge: OSCAR assists. It does not approve or merge.
- Open governance: Under the Linux Foundation, roadmaps, RFCs, and discussions remain public and vendor neutral.
- Traceability: Documentation and pull request notes continue to track what ships.
What changed for the community
- Lower barriers to participation: If you understand the process, you should not be blocked by unfamiliar tooling.
- Easier onboarding for new maintainers: Natural language workflows help more people contribute to release steps.
- Support for the eight-week rhythm while maintaining quality bars.
How it works at a glance
OSCAR connects to the systems that power OpenSearch releases, including knowledge sources, metrics, CI, and communication channels. It uses a guarded set of actions and follows the same community processes that govern releases. For readers who want deeper technical details, an appendix can describe the agent patterns and underlying services.
Architectural overview
Built on Amazon Bedrock agents with a dual-supervisor architecture, OSCAR connects release tasks through a conversational interface. It combines multiple capabilities—metrics analysis, knowledge base queries, Jenkins automation, and cross-channel communication—to provide context-aware responses.
OSCAR’s architecture, shown in the following image, implements a dual-agent security model in which privileged users access full system capabilities while standard users receive read-only assistance, ensuring both accessibility and security.
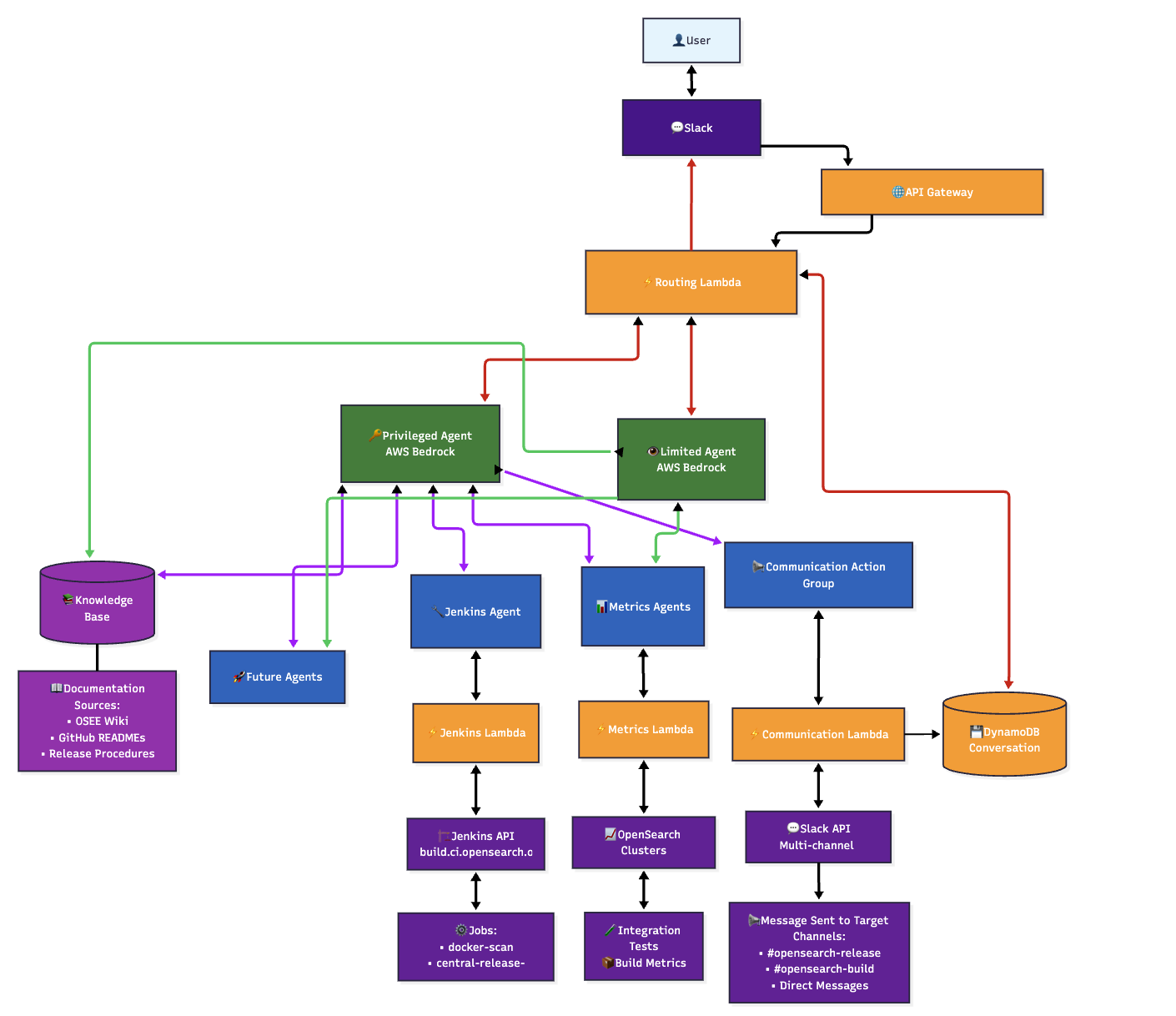
Component flow for a release workflow: Jenkins query
OSCAR employs communication between multiple components, including multiple agents, Amazon DynamoDB, and knowledge bases, as shown in the following image.
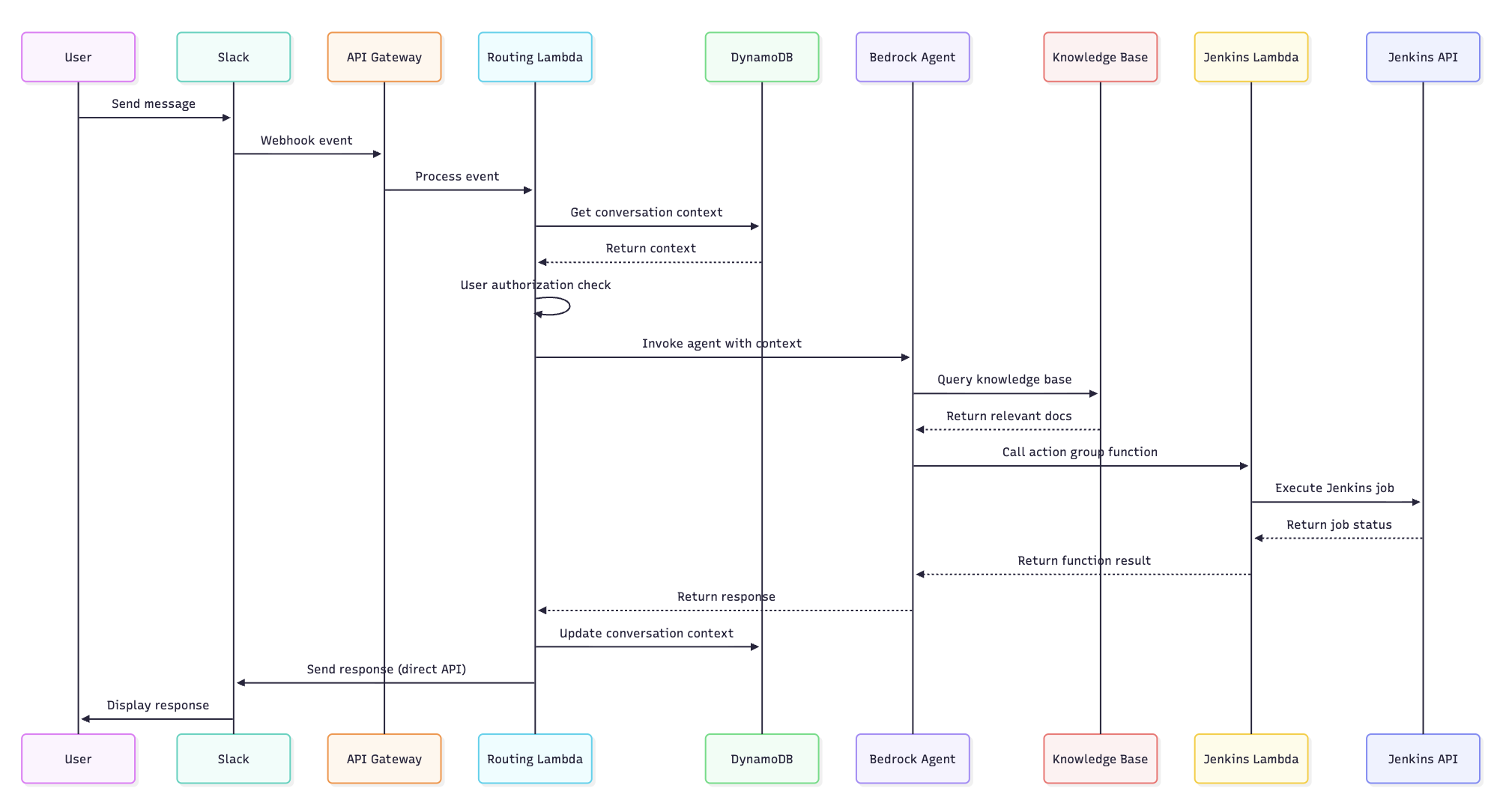
OSCAR in action: 3.2.0 release success stories
During the 3.2 release, we piloted a beta version of OSCAR to handle routine steps using natural language commands. OSCAR demonstrated its value across three critical areas:
- Metrics integration and analysis
- Workflow automation with Jenkins integration
- Release communication automation
1. Metrics integration and analysis
OSCAR transformed how release managers interact with complex build and test data. Instead of manually querying multiple OpenSearch clusters and interpreting raw data, release managers can simply ask: “@OSCAR-beta Show me integration test results for RC 6 on version 3.2.0 for OpenSearch Dashboards.”
OSCAR’s metrics system automatically performs the following steps:
- Queries the OpenSearch metrics cluster for integration-test-related data
- Removes duplicate test results.
- Cross-references release candidate (RC) numbers with specific artifact build numbers
- Generates comprehensive summary reports highlighting critical issues
A sample query and answer are presented in the following images.
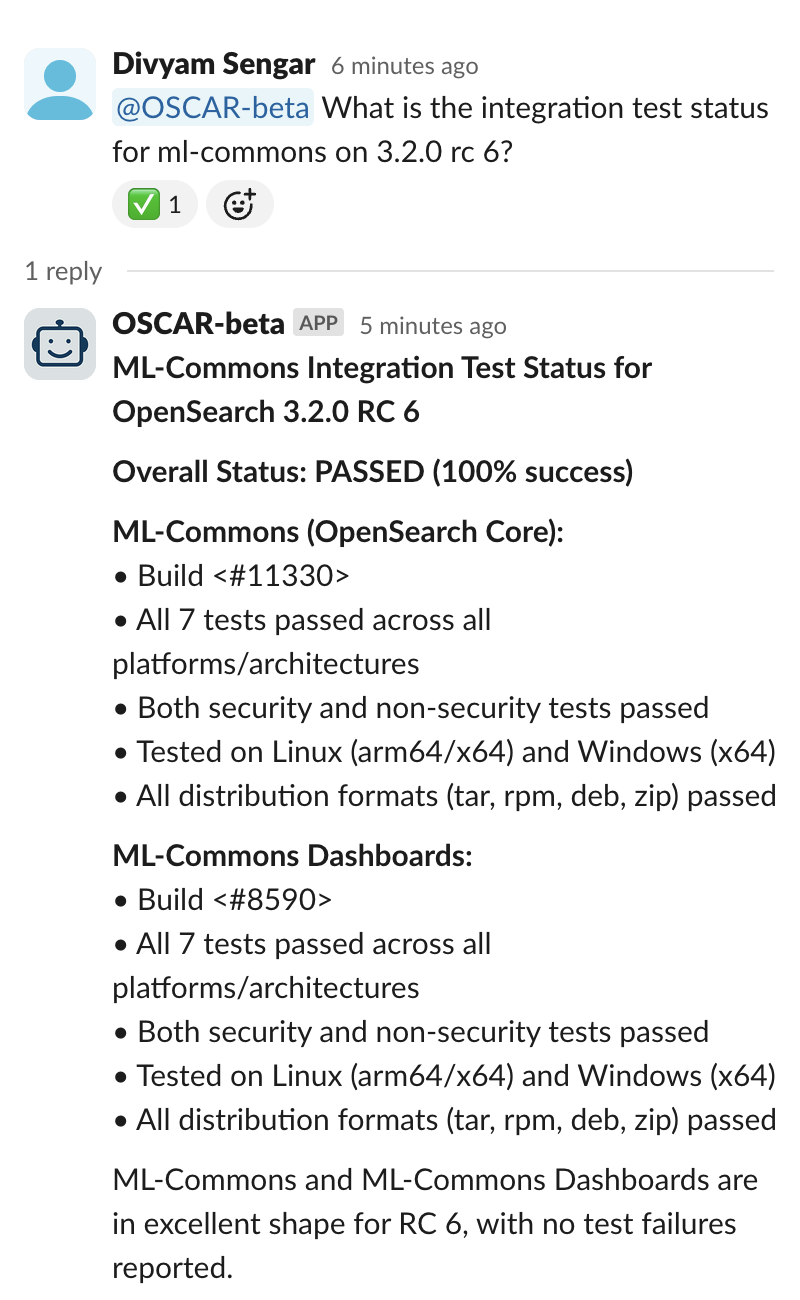
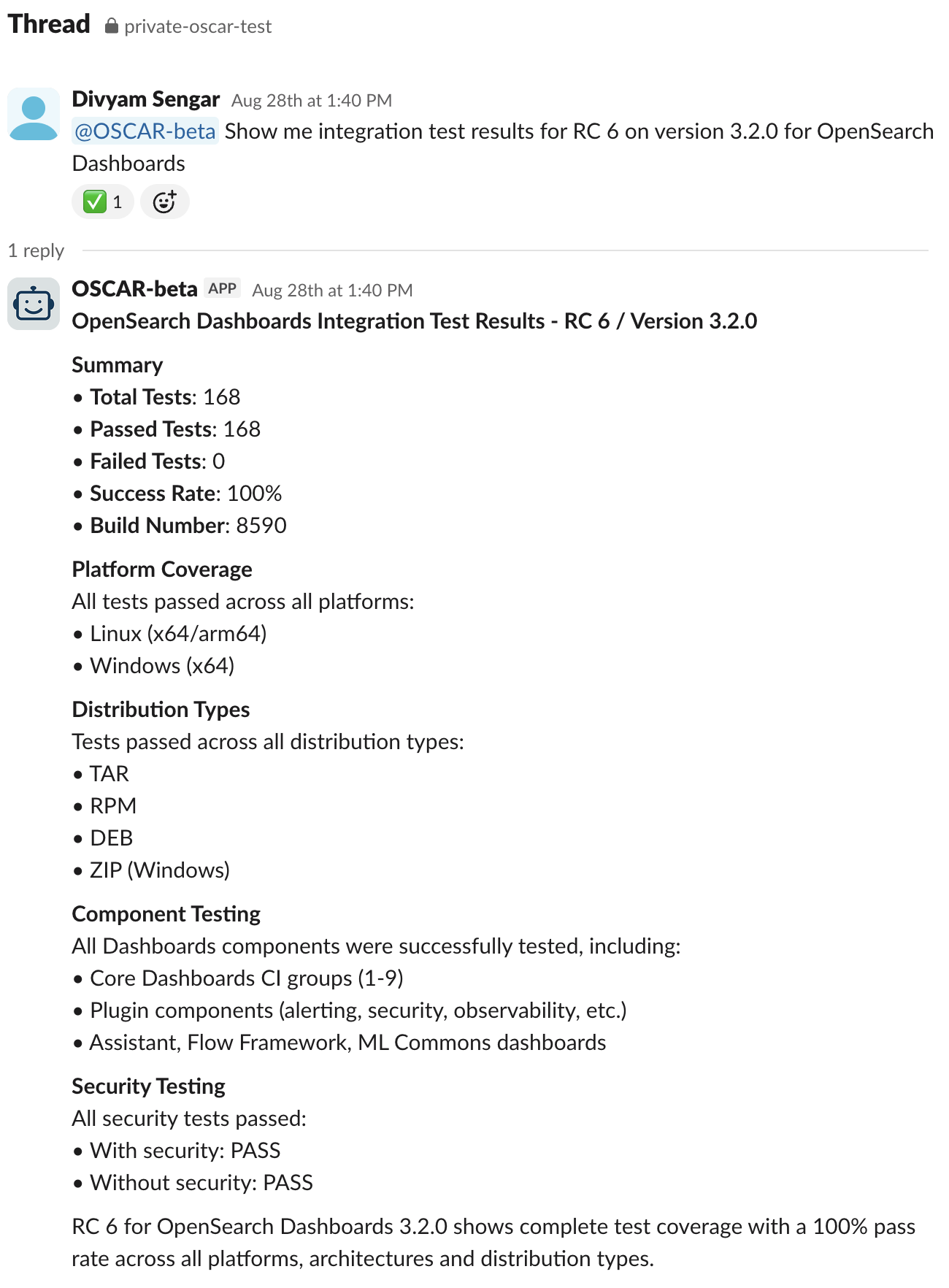
Technical Implementation: The metrics system uses specialized Amazon Bedrock agents (Integration Test Agent, Build Metrics Agent, Release Metrics Agent) that process data from production OpenSearch clusters, ensuring that release managers receive accurate, real-time insights without manual data processing.
2. Workflow automation with Jenkins integration
OSCAR’s Jenkins workflow automation performs the following steps:
- Automatically resolves version
3.2.0to specific RC and build numbers - Prefills complex workflow parameters using historical data
- Implements mandatory confirmation workflows for security measures
- Provides direct links to job execution and progress monitoring
For example, release managers can ask “@OSCAR-beta Run central release promotion workflow on Jenkins with 3.2.0”. An example interaction is shown in the following image.
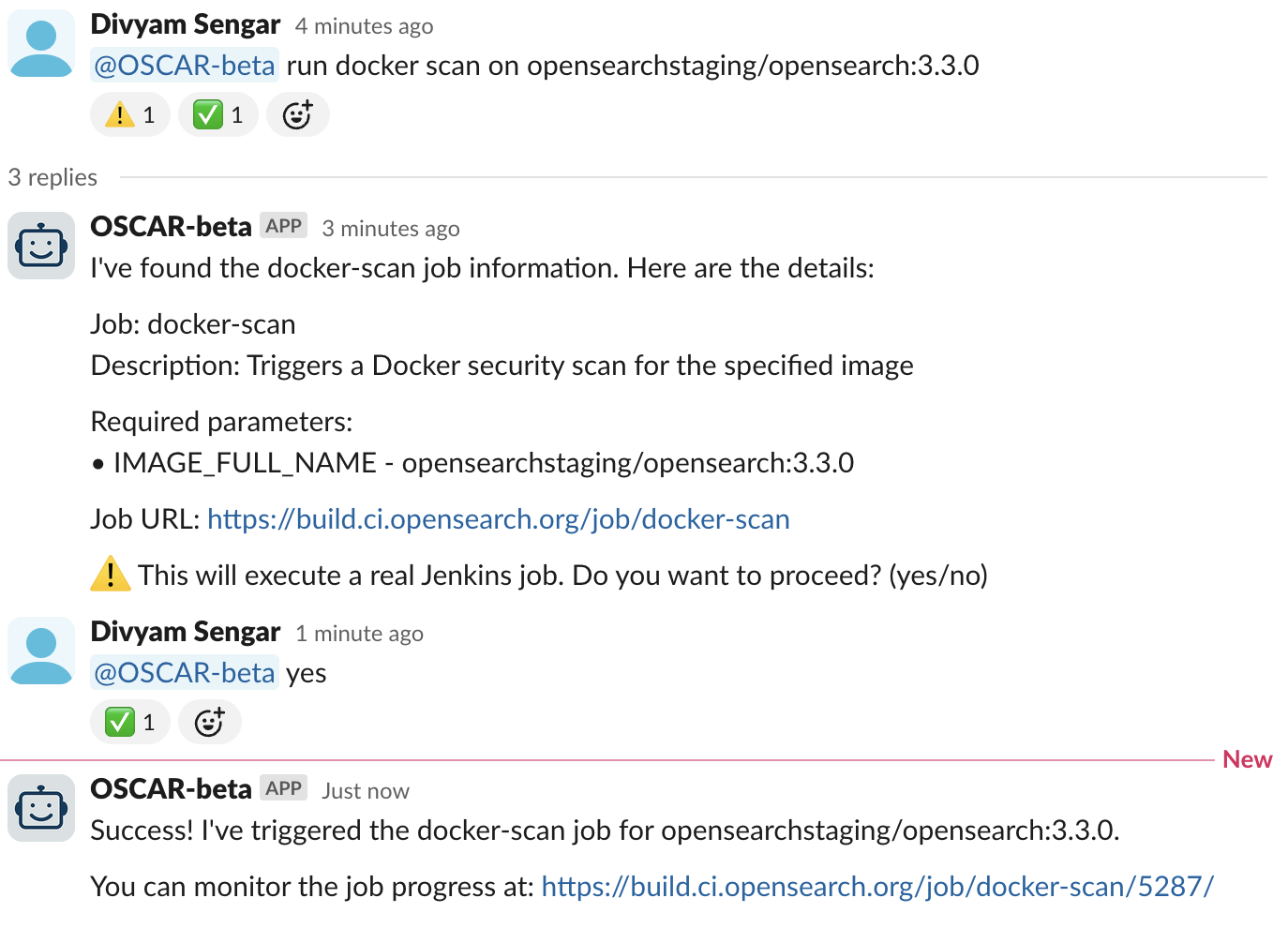 OSCAR triggers Jenkins workflow execution by using natural language with built-in security controls.
OSCAR triggers Jenkins workflow execution by using natural language with built-in security controls.
Security features: All Jenkins operations require explicit user confirmation and are restricted to authorized users through the dual-agent architecture. Every operation includes audit trails with user context for complete accountability.
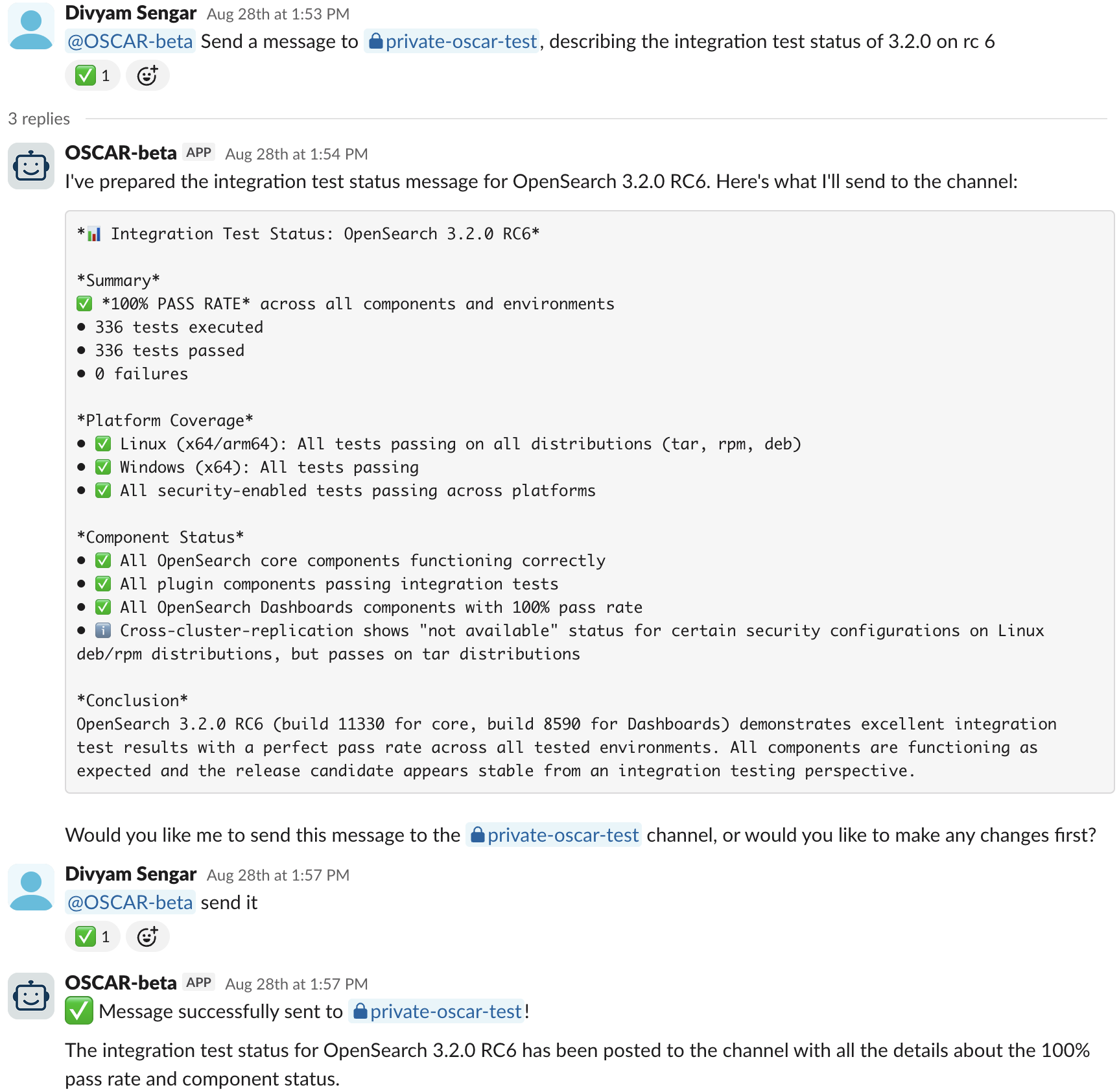
3. Release communication automation
OSCAR streamlines release communications by automating message generation and multi-channel broadcasting.
OSCAR’s release communication automation includes the following capabilities:
- Automated announcements: Autogenerated release announcements using predefined templates combined with real-time metric data
- Integration test summaries: Formatted reports of test results for stakeholder communication
- Cross-channel coordination: Broadcasting consistently formatted messages to multiple Slack channels
- Automated pinging: Automatically identifying and pinging maintainers using metrics queries
A sample communication is shown in the following image.
Development insights: What we learned
While OSCAR’s development progressed smoothly and produced a layered, secure modular architecture, it also required major refactoring once we discovered the complexity of release automation.
Architectural evolution: We started with a simple LLM + knowledge base model but quickly realized that release management required orchestrating multiple complex systems. This drove us toward an agentic approach with specialized collaborators for Jenkins, metrics analysis, and communications.
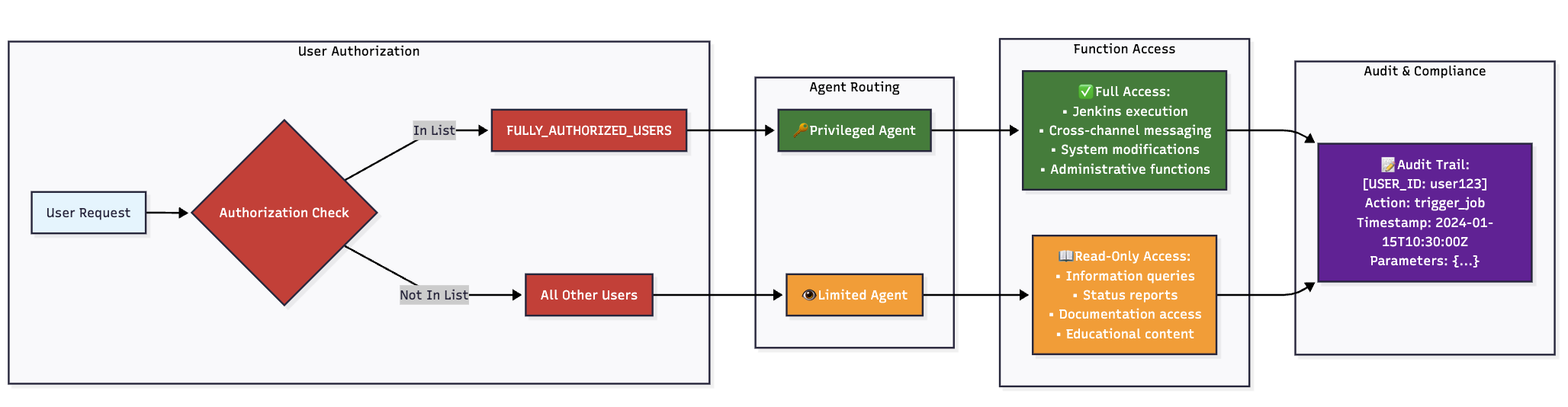
Security-first design: Our dual-agent architecture (privileged vs. limited access) with mandatory confirmation workflows proved essential for enterprise adoption. Implementing security controls from day one avoided costly retrofitting later. The authorization flow is shown in the following image.
 Modular infrastructure: Using AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK) with separate stacks enabled rapid iteration on individual components. The serverless AWS Lambda architecture automatically handled scaling during release periods, while DynamoDB’s Time To Live (TTL) features managed conversation context without manual cleanup.
Modular infrastructure: Using AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK) with separate stacks enabled rapid iteration on individual components. The serverless AWS Lambda architecture automatically handled scaling during release periods, while DynamoDB’s Time To Live (TTL) features managed conversation context without manual cleanup.
Real-world complexity: The 3.2.0 release revealed gaps between assumptions and actual needs. Users required intelligent deduplication, automatic parameter resolution, and context-aware formatting, driving sophisticated query routing and specialized response logic.
Key insight: Successful AI automation for enterprise workflows requires not just intelligent responses but also intelligent orchestration of multiple systems with robust security and deep understanding of operational complexity.
Beta status and public availability
OSCAR is currently in beta, actively supporting OpenSearch release processes while the development team refines features and gathers user feedback. The system has proven its value during the 3.2.0 release cycle, demonstrating significant improvements in efficiency and accessibility.
How can I use OSCAR?
OSCAR supports community contributors, maintainers, and release managers, offering tailored capabilities for each group.
Community contributors
Community contributors can use OSCAR to quickly access guidance, resources, and support that simplify participation in the release process. Here are some example queries:
- Getting started guidance: “@OSCAR-beta I’m new to OpenSearch releases. What’s the current release timeline and how can I help?”
- Release process learning: “@OSCAR-beta Explain the OpenSearch release process and what each RC (Release Candidate) means”
- Documentation access: “@OSCAR-beta What Docker configurations should I use for local testing?”
- Test environment setup: “@OSCAR-beta Help me set up a local environment to test OpenSearch 3.2.0 RC6”
- Community coordination: “@OSCAR-beta Who are the current maintainers for the security plugin and how do I reach them about release issues?”
Repository maintainers
Repository maintainers can use OSCAR to manage releases, monitor issues, and coordinate with contributors efficiently. Here are some example queries:
- Build health monitoring: “@OSCAR-beta Show me failed integration tests for opensearch-dashboards in the last 48 hours”
- Test coverage analysis: “@OSCAR-beta What’s the test coverage trend for security-analytics plugin over the last 2 releases?”
- Performance impact review: “@OSCAR-beta How did my recent changes to ml-commons affect build times and test execution in CI?”
- Release readiness check: “@OSCAR-beta Is my sql repository ready for 3.2.0 release? Show me any outstanding issues or blockers”
- Automated tagging: “@OSCAR-beta Help me create release tags for all my repository branches aligned with OpenSearch 3.2.0”
Release managers
Release managers can use OSCAR to streamline release oversight, coordinate across components, and access detailed metrics. Here are some example queries:
- Release status overview: “@OSCAR-beta What’s the current status of OpenSearch 3.2.0 release? Show me any blocking issues.”
- Cross-component coordination: “@OSCAR-beta Check if all OpenSearch Dashboards dependencies are ready for 2.15.0 RC3 promotion”
- Stakeholder communication: “@OSCAR-beta Send release status update to #releases channel with current test results and timeline”
- Jenkins workflow management: “@OSCAR-beta Trigger component release promotion for OpenSearch 3.2.0 with the latest build numbers”
- Metrics deep dive: “@OSCAR-beta Show me integration test regression analysis comparing 3.2.0 vs 3.1.0 testing status”
Future enhancements
OSCAR’s roadmap focuses on transforming it from a reactive assistant into a proactive, intelligent platform that anticipates issues and automates complex decisions. Enhancements are planned in the following areas.
Predictive intelligence and proactive automation
This feature helps developers anticipate issues and prevent failures before they impact the CI/CD pipeline:
- Build failure prediction: ML-powered analysis of commit diffs and code patterns as they are made in order to predict test failures with sufficient accuracy, alerting developers before CI/CD execution, similar to a predictive GitHub Actions layer.
Advanced decision automation
These capabilities streamline release decision-making and cross-component coordination, reducing manual overhead:
- Automated go/no-go framework: Multidimensional risk assessment combining test coverage, critical issues, and historical success rates in order to drive intelligent release decisions
- Cross-repository coordination: Dependency-aware orchestration across multiple OpenSearch components with intelligent version synchronization
- Stakeholder polling automation: Intelligent Slack-based voting with role-weighted decision algorithms
Security-first release management
These enhancements focus on proactive security, automatically assessing risks and alerting teams to vulnerabilities:
- Real-time CVE impact assessment: Automated analysis of security vulnerabilities with release impact scoring and mitigation pathway suggestions
- Threat intelligence integration: Proactive security notifications using real-time threat feeds
Dynamic knowledge management
These improvements aim to centralize and intelligently surface OpenSearch knowledge, making information accessible and actionable for contributors and maintainers:
- Comprehensive documentation ingestion: Automated ingestion from all OpenSearch repositories, release notes, and blog posts with semantic understanding
- Version-aware knowledge: Intelligent routing of documentation based on user context and version requirements
- Self-healing infrastructure: Autonomous issue detection and resolution with pattern recognition and predictive maintenance
Public Slack integration
- The beta version of OSCAR is now available in the public OpenSearch Slack channel release-bot-oscar. You can use @oscar-beta for channel interactions. The bot is still in development, so not all features are available yet. If you have any feedback regarding OSCAR’s performance, please let us know with a comment in the same channel.
Upcoming milestones
These are the next steps in rolling out OSCAR to the community, expanding access, and improving adoption:
- Community access: Expanded access for external contributors and community release managers
- Enhanced documentation: Comprehensive guides for community adoption and contribution
We’re committed to maintaining OSCAR’s pioneering approach while ensuring stability and security as we expand access to the broader OpenSearch community. If you contribute to OpenSearch, try a release task with OSCAR as your assistant. If you are new to release management, pair with a mentor for your first step. If you run release management in another community, bring your best ideas to our RFCs. Together we can keep the cadence, raise the quality bar, and make participation easier for everyone.





